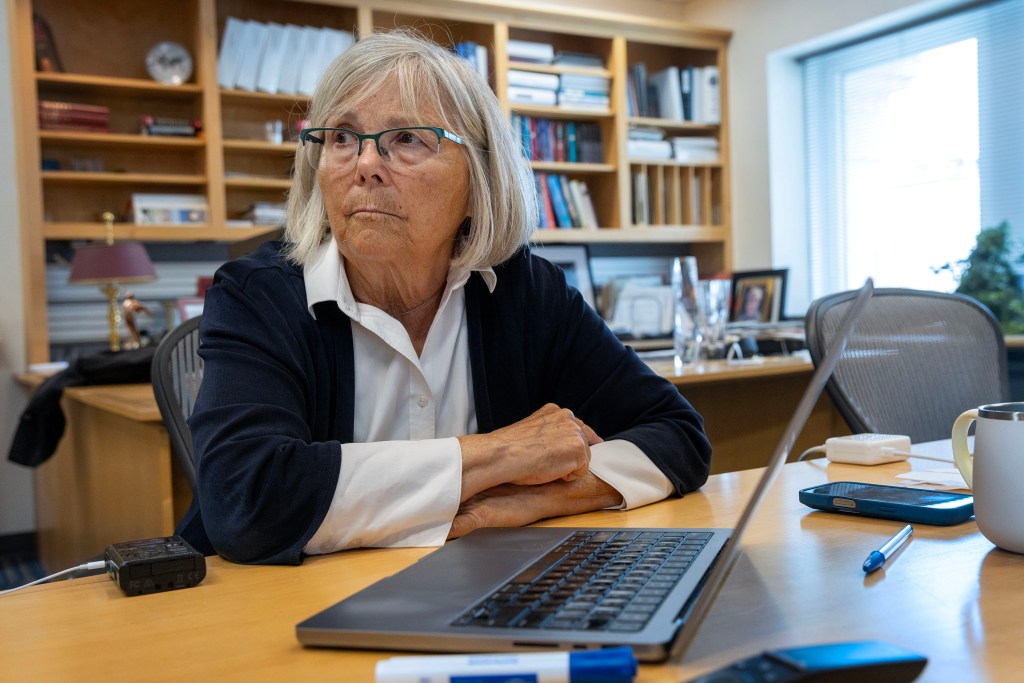
The Department of Health and Human Services acknowledges a troubling reality: bureaucracy is stifling progress. For too long, vital work has been overshadowed by red tape, hindering the potential of groundbreaking innovations, particularly in the realm of artificial intelligence. The promise of faster drug approvals, a key goal outlined in their Strategy for Artificial Intelligence, hangs in the balance.
History reveals a consistent pattern. It isn’t the inherent difficulty of scientific challenges that slows medical advancement, but rather the accumulation of regulations. A creeping regulatory burden threatens to diminish AI’s transformative power in drug discovery and development. To avoid repeating past mistakes, a radical shift is needed – a complete reassessment of how new technologies are brought to market.
Medical innovation has fallen behind other sectors. While breakthroughs like antibiotics once rapidly reshaped healthcare, the pace of progress has dramatically slowed. One expert observed that medicine in 2020 felt closer to 1970 than to 1920, a stark illustration of this stagnation. The question isn’t simply about the complexity of the human body, but about the obstacles placed in the path of innovation.

Consider the development of 4G communications – a mere decade from initial discussions to widespread commercial use. This rapid advancement stands in stark contrast to the lengthy timelines common in the medical field. This comparison highlights the impact of regulatory processes on the speed of innovation, offering a crucial benchmark for evaluating the future of AI in healthcare.
The Human Genome Project, a monumental scientific achievement, initially thrived under a flexible framework focused on data sharing and ethical considerations. It completed its ambitious goals two years ahead of schedule, proving that scientific complexity isn’t always a barrier to rapid progress. However, the story changed once the project’s findings moved toward practical application.
The transition from genetic mapping to drug development revealed a significant slowdown. It took eleven years after the discovery of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology to achieve the first FDA approval. Even then, the FDA acknowledged the need for greater clarity in its processes, a tacit admission of the challenges innovators faced. A backlog of research and trials continues to grow, inevitably leading to further delays.
The experience with stem cell research offers another cautionary tale. A company, Geron, invested heavily in early research, navigating a complex regulatory landscape and incurring massive costs. Despite promising pre-clinical results, the program was ultimately abandoned due to financial constraints, demonstrating how regulatory burdens can indirectly stifle innovation by making it economically unsustainable. The company eventually found success in oncology, but only after 34 years of research.
The case of 23andMe, a pioneer in direct-to-consumer genetic testing, illustrates how regulation can extend its reach into the realm of information itself. The FDA initially deemed the provision of genetic insights a regulated “device,” requiring approval for each individual report – a practically impossible task. While the company eventually gained approvals, the initial regulatory overreach altered its trajectory and ultimately contributed to its recent bankruptcy.
These examples – the Human Genome Project, stem cell research, and personal genetics – reveal a consistent pattern: years of scientific discovery followed by decades of regulatory review. The financial markets are now closely watching how AI will be regulated, anticipating potential delays and uncertainties that could impact the development of AI-driven healthcare solutions.
Currently, the FDA requires AI-discovered drugs to undergo the same rigorous clinical trial process as traditional pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, a new seven-step framework for AI submissions demands extensive documentation and risk assessment. While ensuring safety and effectiveness is paramount, these requirements add layers of complexity and potential delay.
Adding to the uncertainty, concerns are emerging about liability for clinicians using AI tools that haven’t received full FDA approval. This ambiguity creates a chilling effect, potentially hindering the adoption of AI in clinical care. The HHS faces a critical decision: will it proactively foster innovation, or will it impose regulations that stifle progress?
A zero-based regulatory approach offers a path forward. This means starting with a clean slate for each new technology, focusing only on the essential requirements for demonstrating safety and effectiveness. Regulators should avoid involvement in early-stage research, limiting documentation to specific, necessary criteria. This streamlined process would free up valuable FDA resources.
This isn’t deregulation, but *precision* regulation. AI itself could be leveraged to automate auditing, identify key variables, and provide real-time data feeds to the FDA. This would enable faster, more accurate assessments and allow regulators to focus on areas of genuine concern. An annual review process could further refine these requirements based on experience.
The greatest threat to AI’s potential in healthcare isn’t the complexity of the science, but the weight of regulation. A shift towards a zero-based approach is essential to unlock innovation, accelerate development, and deliver transformative solutions to patients. The leaders at HHS have the power to chart a new course.
By embracing a more agile and focused regulatory framework, the FDA can transition from a gatekeeper to a real-time auditor of scientific progress. This would allow them to observe and assess a wider range of innovative developments, fostering a virtuous cycle of innovation and improvement. The time to act is now, before the initial timelines for AI-driven healthcare solutions are missed.